3D printing is a superbly growing technology in the modern printing world. It enables professionals and newbies to handle high current loads in high-volume printing. How much electricity does a 3D printer use- this is equally important for the users like the printer cost and print materials.

Do you know about the factors that affect the electricity consumption of a 3D printer? Besides, have you ever thought of how you can reduce heat loss in regular 3D printing?
Don’t worry. This article will let you know the ins and outs of 3D printing and its electricity consumption rate. We hope it will help you optimize the printing cost to a large extent.
Let’s make a move.
- Specifications of a 3D Printer
- Do 3D Printers Use a Lot of Electricity- Reality or Myth
- How much power does a 3D Printer Use Per Hour
- Components Responsible for High Power Consumption of a 3D Printer
- Factors that affect Power Consumption in 3D Printing
- How to Calculate your 3D Printer’s Power Consumption
- How much does it Cost to Run a 3D Printer
- The Way you can Reduce Electricity Costs with a 3D Printer
- Tips for Safe Use of a 3D Printer
- Final Words
Specifications of a 3D Printer
A 3D printer’s features are compatible with modern printing technologies. In particular, their electricity usage monitor, heated build plate, and compatibility with versatile filaments are highly impressive.

| Average Build Volume | 10 x 6.0 x 6.7 in |
| Cloud Printing | Enabled |
| Build Plate Material | Glass |
| Heated Build Plate | OK |
| Filament Compatibility | PLA, ECO-ABS, PETG, Nylon |
Do 3D Printers Use a Lot of Electricity- Reality or Myth
3D printers bring out an outstanding change in the FDM printing world. But do 3D printers consume a lot of electricity during their operation?
Usually, these printers don’t consume a high amount of power like other appliances. For example, a typical desktop computer, air conditioner, heater, etc consumes more heat than 3D printers.
Besides, the build volume and Z-axis printing significantly reduce the power bill and heat losses. So, this is not entirely true that 3D printers require high power usage.
How much power does a 3D Printer Use Per Hour
A 3D printer’s maximum consumption varies depending on the heating element, printing temperature, high-temperature filaments, etc. But how much power does it consume? Is its average power consumption higher than other home appliances?
This chart will be helpful for you to get a better understanding of this issue-
| Device | Energy Usage |
| 46 Inch LED TV | 60-70 Watts |
| Incandescent light bulb | 60-100 W |
| 3D printer (while printing) | 50-150 W |
| Typical desktop computer | 100-450 W |
| Inverter air conditioner | 1300-1800 W |
| Space heater | 2000-5000 W |
Components Responsible for High Power Consumption of a 3D Printer
Components of a 3D printer are designed to handle high mechanical, thermal, and electrical pressures. During their functioning, some components consume a huge amount of electric power resulting in high electricity costs.
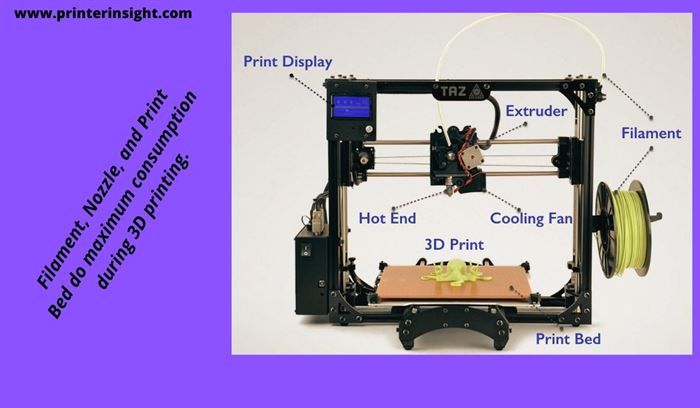
That’s why it is necessary for a user to be aware of power-consuming elements that cause extra cost. Do you know about them?
Don’t worry. We are here for your convenience. Let’s have a look at the following heating elements of a consumer-grade 3D printer-
- Printer Hot End
- Build Plate
- Stepper Motor
- Control Board
- Fan
- Display
Factors that affect Power Consumption in 3D Printing
Heating at Hot End
A 3D printer’s hot end is one of the most power-consuming components. Here, you can find a nozzle that is usually effective for melting the filament. Overall power consumption of a 3D printer basically depends on the type of filament you are using in this section.
Some condensation plastic filaments like Nylon-66, Nylon-6, etc consume a high amount of electricity because of their high-temperature functionalities.
Besides, a popular thermoplastic named ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) causes high heat. This terpolymer promotes high power consumption in the hot bed of a 3D printer. To get a better idea of this topic, you can check this article on the Energy consumption of common desktop additive manufacturing technologies.
That’s why you need to use these filaments in a controlled way so that you can resist a heavy current consumption in a single portion of the entire 3D printing.
Heating of the 3D Printer Bed
If you dig into the functional properties of 3D printing, you can find a close interconnection between the temperature of the print bed and the nozzle. The heating of a 3D printer’s print bed is related to two different factors. These are-
- Printer bed size
- The temperature of the heated bed
Impact Of The Printer Bed And Temperature
It is obvious that a large heated bed of 3-dimensional printers requires high power usage to control the temperature demands of printer components. This phenomenon leads to high power costs. That’s why you have to consider the printer size in this case because it has a significant impact on the size of the heated bed.
How much temperature you should set in 3D printing relies on the filament’s type. At that point, the printer nozzle matters a lot.
Usually, 3D printing suffers a lot from warping and low adhesion on the heated bed. These two phenomena decrease the printing quality to a large extent.
But you can handle them by linking the temperatures of the nozzle as per your requirement. It improves bed adhesion and the overall functionality of your 3D printer in high-volume printing.
Cold Printing
This issue remains unnoticed in most cases. But cold printing is a vital issue in the world of 3D printing. When you are concerned about how much power a 3D printer draws, this is undoubtedly a burning question. Do you know what cold printing is?
3-dimensional printers are usually made of metals that become cold during the printing process. These metallic components promote condensation that results in the accumulation of water on the insulation materials and the printer surface.
In the results, they take more time to be heated when you power the printer running at a low wattage. It is just like a warm-up time for 3-dimensional printers. If this period extends to a certain degree, the power usage will be high and you can’t lower electricity costs.
Besides, some heating elements release flammable gases. These gases cause serious hazards in your 3D printer which also increase the average power draw and electric bill to a certain extent.
Heat Loss
Do you know how much temperature a 3D printer component can handle?
It’s almost 200⁰C. As it is highly important to maintain this temperature range, sometimes they cause heat loss.
Moreover, printer nozzles and print beds with high temperatures cause a significant heat loss. This heat loss impacts all the costs. So you have to pay close attention to reducing the heat losses to keep the electric bill within your limit.
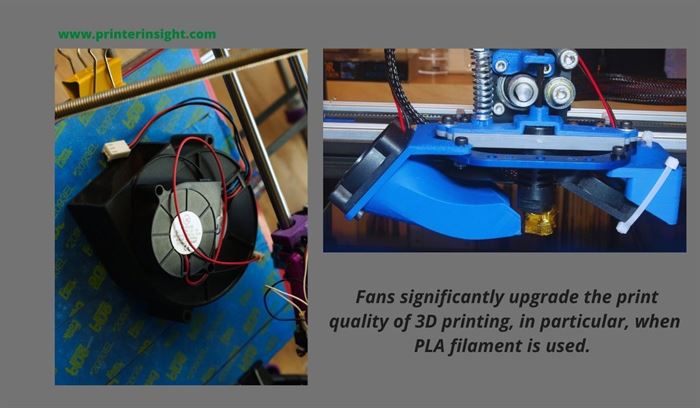
Number of Fans
In most cases, 3D printers incorporate a minimum of 3 fans. These fans are designated for the following tasks-
- Lowering the filament temperature
- Regulating the temperature of the nozzle by cooling down the heat sink of the printer’s hot end
- Regulating the mainboard temperature
Printer fans are small in size. But they consume significant power in the long run. That’s why you should not ignore this matter.

3D Printer Power Supply
Power usage and supply have a crucial part in 3D printing. Normally, 3D printers are compatible with external power sources along with a self-made power supply.
When the electricity bill is concerned with 3D printing, the self-produced power source is more efficient compared to an external source. It happens due to the dependency of external power sources on the alternating current. It causes a high power draw during the printing process.
Besides, self-powered 3-dimensional printers ensure a consistent power supply which is useful for drawing less power and reducing the total cost of electricity.
If you intend to use an external power supply, make sure that your printer supports solar cells or battery backup. It helps not to be dependent on the traditional power supply and decreases total cost.
Control Board
This is the mastermind of a 3-dimensional printer. Usually, the control board consists of multiple electrical components that act to control printing temperatures, printing speed, battery backup, etc.
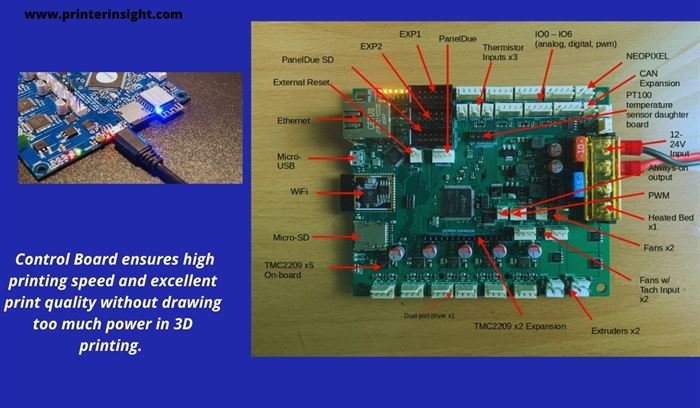
Besides, the control board of a 3-dimensional printer controls the nozzle placement, functions of extruder gears, and many more. Though it offers a lot of activities in 3D printing, it consumes less power compared to both the nozzle and print bed.
That means the control panel is supportive of reducing the actual cost due to the power draw during 3D printing.
Layer Thickness
Concerning power efficiency, 3D printers are compatible with versatile filament materials. These coating materials play a huge role in promoting average power consumption during 3D printing.
Usually, PLA materials consume as much power as ABS materials. PLA is reputable among regular 3D printer users for its low power consumption (5W). But it has a drawback of taking more time for heating up.
On the contrary, ABS materials, operating at a higher temperature, require high wattage with respect to their layer thickness (20W/mm). That’s why you need to pay a high electricity cost when you are dealing with ABS materials.
Moreover, there is always a risk of burning out printer components at high temperatures while using ABS materials. So, PLA materials are preferable to ABS concerning these issues.
But you can still use ABS materials in 3D printing. Do you know how?
You just need to choose a 3D printer that is programmable with lower temperature layers and less aggressive. This can lower energy costs to a large extent. Doesn’t it sound fantastic?
Stepper Motors
Do you have any idea how Stepper motors affect 3-dimensional printers to deliver quality printing?
Stepper motors are a very crucial element of 3D printer power supply. These motors are not very heavy. Most noteworthy, their power draw is supportive of low power expenses.

In most cases, these motors are used in controlling the nozzle movement as well as driving the extruder gears in a completely systematic way. There is one vital thing that you have to consider during operating these stepper motors.
Stepper motors need to run without any interruption until the completion of the entire 3D printing. Otherwise, you don’t get the optimum output from these motors and they can malfunction after a couple of cycles. Don’t you think that’s a bad sign for your 3D printer?
Off course. Wrong use of a stepper motor can’t control the nozzle temperature as per your demands which leads to consumption of more electricity. So, you must pay attention to this issue closely.
Number of Extruders
The more the number of extruders used in the 3D printing process, the more the print quality improves in multicolor printing. Because extra extruders help improve the functionality and durability of 3-dimensional printers to a certain degree.
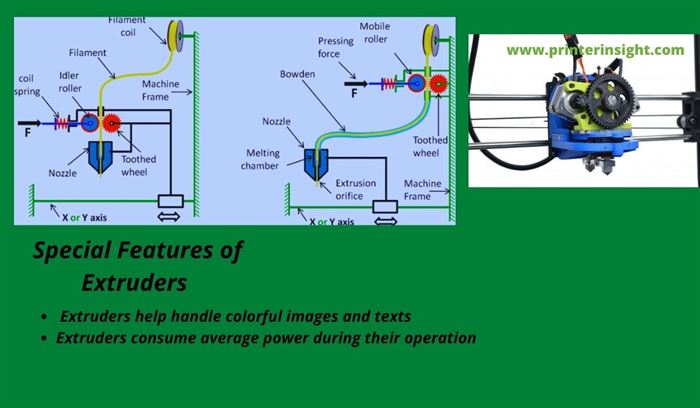
But additional extruders require more electricity which impacts other costs as well as the power expenses. So, you must be conscious while incorporating extruders in your 3D printer.
Number of Hot-Ends in Use
How many hot ends you need to apply is related to the number of extruders. If you imply a lot of hot ends during the printing process, they consume a huge amount of power. Then the power bill will be significantly high. That’s why you have to use the number of hot ends in a controlled manner.
It is obvious that print bed temperature and the nozzle temperature are the prime causes of the 3D printer power consumption. So, you need to focus on these issues seriously to reduce power consumption.
How to Calculate your 3D Printer’s Power Consumption
Have you ever thought of how much electric energy a 3D printer consumes daily?
It’s very simple.
Electric power = current x voltage.
You just need to find out the Voltage and Ampere ratings of your 3D printer to calculate how many watts a printer uses. Besides, you have to know the operating period of your printer. After gathering this information, just follow the formula given below-
Energy Consumption = (VI/1000) tn
Here, V= Voltage Rating
I= Current Rating
t= Operating Time
n= Number of 3-dimensional Printers
For example, if you run a 3D printer at 200V and 0.76A for 6 hours daily, the consumed energy will be (2000.76/1000) 61)= 0.912 Kilowatt-hour.
3-dimensional printers consist of an electricity usage monitor where you can easily find out how much power your printer consumes daily.
How much does it Cost to Run a 3D Printer
When you are sure about how much electric does a 3D printer use, you can easily calculate the electricity cost and overall cost of this machine.
Electricity Cost = Energy Consumption Cost Per Unit (Kilowatt-hour)
Then, you just need to add the maintenance cost and printing cost to find out the overall cost of using a 3D printer. Isn’t it very simple?
Nowadays, 3D printer electricity cost calculator makes your job easier. You just input the values of required ratings and this calculator handles the rest.
The Way you can Reduce Electricity Costs with a 3D Printer
Worried about more power usage in 3D printing?
Don’t be so. You can significantly reduce 3D printers like Ender 3 V2 power consumption if you follow some rules. Such as
Gear Up The Print Speed
You can easily adjust the print speed of your 3D printer which results in reducing energy costs. But how can it be possible?
Very simple. Just follow the instructions given below-
- Improve the brim speed
- Decrease the infill amount
- Use zigzag or line infills
- Increase the nozzle temperature
- Upgrade the layer height and travel speed to a certain extent
- Lowering the shell size concerning the dimension of the nozzle
These instructions may hamper the print quality in some cases. That’s why you need to make a balance between the print quality and speed of your printer to get the optimum result.
You can make printer print faster by following some guidelines and that will be a great help for you in this case.
Using Print Bed Enclosures
Print bed enclosures have a significant impact on controlling the print bed and nozzle temperatures. In the case of low-cost 3D printers, this feature is not available often. But you can manage it with plastic sheets and wooden frames.
It resists more power consumption. So, it’s not very tough to lessen the extra cost, isn’t it?
Shortening the Printer Time
If you can shorten the printing time, it will be easier for you to lessen the power cost to a certain extent. It will lead to bringing down the power bill.
Filament Selection
This section is highly important for a professional user of 3D printers. You need to avoid high-temperature filaments like ABS if you intend to curtail your electricity cost. Besides, consider the nozzle temperature and print bed temperature while choosing the filament for your 3D printer.

Using Lightweight Printer
This is very evident that a large printer comes with a large print bed and extra heating elements. Multiple electrical components increase your 3D printer’s power consumption rate. That’s why you need to choose a printer that offers a low footprint.
Lowering the Print Volume
Are you dealing with budget constraints? But still, trying not to compromise with print quality?
Then lowering the print volume is the best option for you to reduce the electricity cost. That means you need to deal with low-volume printing. But this is not a feasible solution to reduce your printer’s average power draw in the long run.
Using a Larger Nozzle
Usually, a 3D printer consists of nozzles of almost 0.4mm. This dimension is useful for extruding down to 0.2mm.
The main benefit of using a large nozzle is to increase the printing speed and control higher temperatures which result in reduced power consumption during 3D printing. That’s how using a larger nozzle reduces other costs due to 3D printing.
Tips for Safe Use of a 3D Printer
- It should be kept in a covered zone during its operation.
- Use a flawless switch circuit
- Ensure a consistent power supply
- Maintain the optimum current load to avoid the voltage fluctuation
- Clean the machine on a regular basis
- Avoid using high-temperature materials
Final Words
Now you have known the ins and outs of how much electricity does a 3D printer use. There is no doubt that 3D printers are beneficial to users for large-scale printing. But printing costs, in particular, the electricity costs matter a lot in 3D printing.
You need to focus on the critical factors that impact resin 3D power consumption a lot. Then you can optimize the printing through a 3D printer.
If you have more queries, please leave a comment. Happy printing.




