A filament printer is the best option if you want to construct large 3D-printed things or if you want to complete your prints.
A resin or SLA/DLP printer is recommended if you would like productivity levels out of another technology or if you would like to generate small objects with a lot of detail. But is there any factor that distinguishes between Filament vs Resin 3D Printer?
This article will render you the entire scenario of the 3D modeling world. Let’s start.
- How Filament 3D Printer Works
- How Resin 3D Printer Works
- What Is SLA/DLP Printing?
- What Is FDM Printing?
- Difference between Filament and Resin 3D Printer- A head-to-head Comparison
- Resin vs Filament 3D Printer- Which System is Most Effective for Your Requirements
- Filament Features for FDM 3D Printing
- Resin Features for SLA/DLP Printing
- Best Filament 3D Printer in 2023
- Best Resin 3D Printer in 2023
- FAQ
- Conclusion
How Filament 3D Printer Works
Filament 3D Printers create 3D parts by burning plastic and spreading it in many stacking plain cuts, or stages. Every plate is formed by shifting the nozzle along the predetermined path and depositing liquid metal.
The nozzle is raised up after each layer is done, and then the next surface is formed above top of the previous one until a complete 3D part is formed.
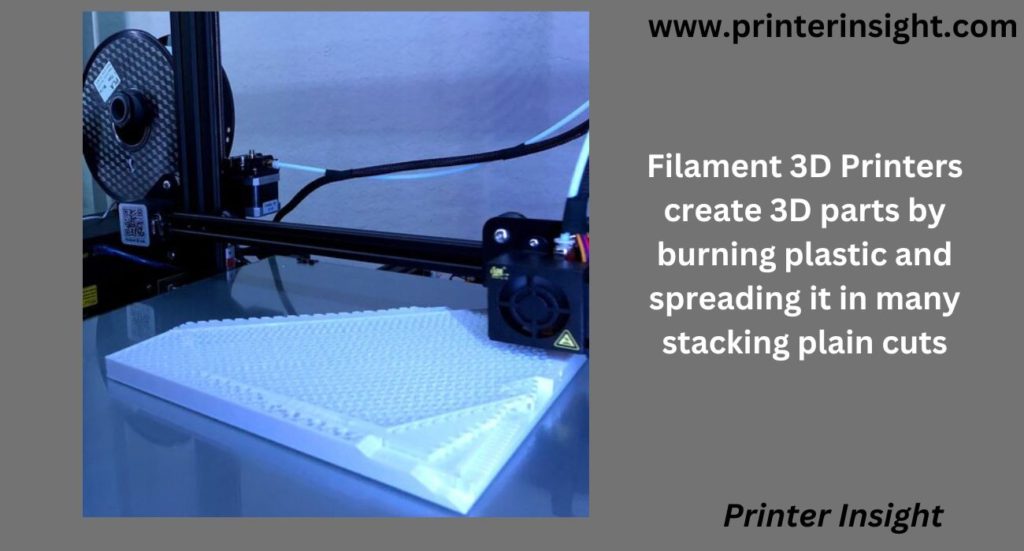
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) and FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) are two terms used to describe Filament 3D Printers. These are two terms that are often used identically.
How Resin 3D Printer Works
Resin printers create items out of liquid resin that forms (solidify) when applied externally. Resin printers manufacture parts in layers in the same way as Filament 3D Printers do, but they do so by submitting individual layers to a grid of UV light to fix the resin in the required spots.
DLP (digital light processing) and SLA (synthetic light amplification) are the two most frequent resin printers.

In terms of how companies process the resin, that varies. SLA printers employ a concentrated ray to retrace a channel throughout every surface, while DLP printers use a UV LCD screen (effectively a mini display) to fix a topmost layer instantly.
These printers have a close similarity from either the outer.
What Is SLA/DLP Printing?
3D printers that use lasers to fix adhesive into stages are classified as stereolithography and digital light processing (SLA/DLP) printers.
What Is FDM Printing?
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is the printing technique most people can identify with. A filament 3D is a strand of plastic that is warmed and put on the prepared surface using only steamy ends.

Difference between Filament and Resin 3D Printer- A head-to-head Comparison
| Topic | Filament 3D Printer | Resin 3D Printer |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Moderate |
| Durability | High | Standard |
| Usability | Useful for beginners | Complicated |
| Build Volume | Large | Small |
| Print Quality | Moderate | High |
| Print Speed | High speed for single object | High speed for multiple objects |
Resin vs Filament 3D Printer- Which System is Most Effective for Your Requirements
When deciding which of these systems is ideal for your purposes, there are several points to consider.
Print Materials
FDM printers are compatible with a wide variety of thermoplastic materials like PLA, Nylon, ABS, PETG, TPU, PA, etc. These materials come with a lot of color combinations and blend like wood-fill, metal-fill, etc.
In contrast to this, resin printers come with a vast variety of aterial formulations and properties. You can find hard and soft resin materials, mechanically stable, filled with additives, etc. So, what is your requirement?
If you require a variety, FDM is the best option. On the other hand, resin 3D printers are a good choice for ensuring various properties in 3D printing.
Print Quality
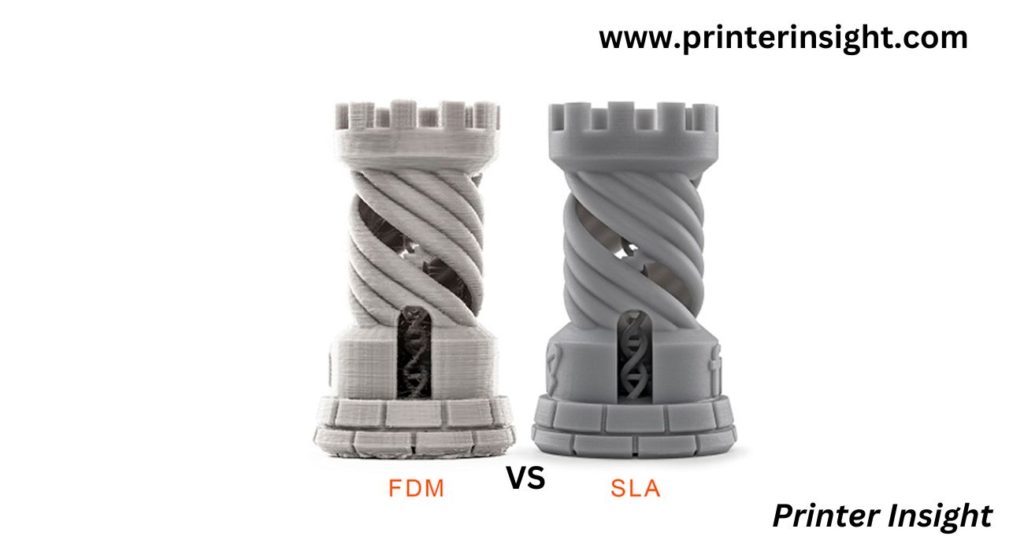
Resin printers are noted for their excellent surface texture, which includes the authority to overcome fine details on images as well as the way to generate structures without a position as a leading line.
Resin prints include levels but are usually invisible to the human eye because they are so small. Every surface on a resin printer is approximately 20-45 thickness in microns. Meanwhile, the levels on a filament 3D printer are often 90-250 thickness in microns.
Because the density for every level is controlled either by the width of digits, mostly on the LCD screen, which is approximately 70 microns for retail DLP 3D printers, resin printers may preserve ultra-delicate information.
The size of the aperture in the nozzle where the burned sample is placed, which is approximately 0.5 mm, limits the sharpness of Filament 3D Printers. On Filament 3D Printers, lower nozzles can be placed, although the small storage nozzles are nevertheless 150 microns.
The filament 3D printer’s manufacturing speed will be extended, though with quite a nozzle.
Resilience Of Printed Parts
Typical resin prints are fragile, making them unsuitable for functioning components subjected to significant drivers. Furthermore, because the resin is UV responsive, contact with daylight damages the images.
However, there are large resins currently on the market that could help resin prints hold up better. However, we’ve discovered that somehow this resin is hard to truly remove off particles and occasionally creates an adhesive mess.
We’ve had greater success merging this resin with several other resins to reduce the adverse effects despite high stiffness. Overall, filament 3D manufacturing is a useful option for workpiece material just because it offers an extra range of motion for varying lengths.
Frequency Of Copying
Filament 3D Printers
Filament 3D Printers can manufacture products standardized way faster with post-processing. As you can guess, the published speed would rise accordingly as you put extra objects towards the printing surface.
This is due to the fact that the nozzle needs to detect individual portions separately.
Resin Printers
Resin printers, on the other hand (particularly DLP printers), may create several things at the same time as a particular object. That’s because the LCD is revealed to every surface for a set time, despite how many components are printed.
In these instances, the resin can frequently be significantly quicker than when a large number of parts are required.
The small print bed limits this, but one benefit of wider resin printers, much like Elegoo Saturn, seems to be that its following points allow users to generate a large number of components swiftly.
Resin vs Filament 3D Printer Speed
Resin 3D printing is comparatively faster than Filament-based 3D printing for multiple objects.
But FDM is not a bad option for single object 3D printing.
The 3D printer speed mostly depends on the size of the printed item and layer height. Usually, a large 3D element with a small layer height takes more time to be printed. Besides, high infill density is responsible for a longer printing period.
In the case of LCD and DLP resin printing, the entire layer is solidified within a short time (2-10 seconds). Here, the amount of resin used per layer has no significant impact. That’s why 3D printing takes less time with resin printers compared to FDM printers.
Initial Assembly And Setup
The majority of filament printers demand considerable setup. However, the level of effort varies. Printers like the Creality CR-10 and Ender 3 Max consist of pre and require about 10 minutes to put together.
Relatively small printers, like the Ender 3 V2, come in further parts and require about 60 minutes to put together. After the printable surface has been completed, balancing it can be a bit of a process of interpretation.

Due to their small size, resin printers are often shipped practically completely built. The only assembly required for the Elegoo Mars we used was placing the printable surface component onto the printers.

Usability
FDM is a better option for 3D printer users, especially for beginners. In this case, loading the filament, starting printing, and removing are pretty easy. But FDM printers demand high-class maintenance and calibration to avoid stringing, warping, and elephant’s foot.
On the contrary, resin printers require an extra bit of care and safety to resist the toxicity of resin elements. These printers consist of hoods to cover the resin vat and resist UV rays. Handling of resin printer hood is troublesome. Moreover, the disposal of additional resin is a hectic task for beginners.
That’s why resin printers are not as user-friendly as FDM 3D printers.
Configuration Of Program
Once constructed, learning all of the many parameters offered for filament printers in the inkjet slicing program to obtain the greatest professional results might require some practice.
Although many current slicers, such as PrusaSlicer and Cura, include prepared settings like most Groups tended machines, knowing how well the individual configurations perform is still vital because tweaks are frequently required to improve printing for specific sorts of structures.
It’s far too simple to program a 3D printer.
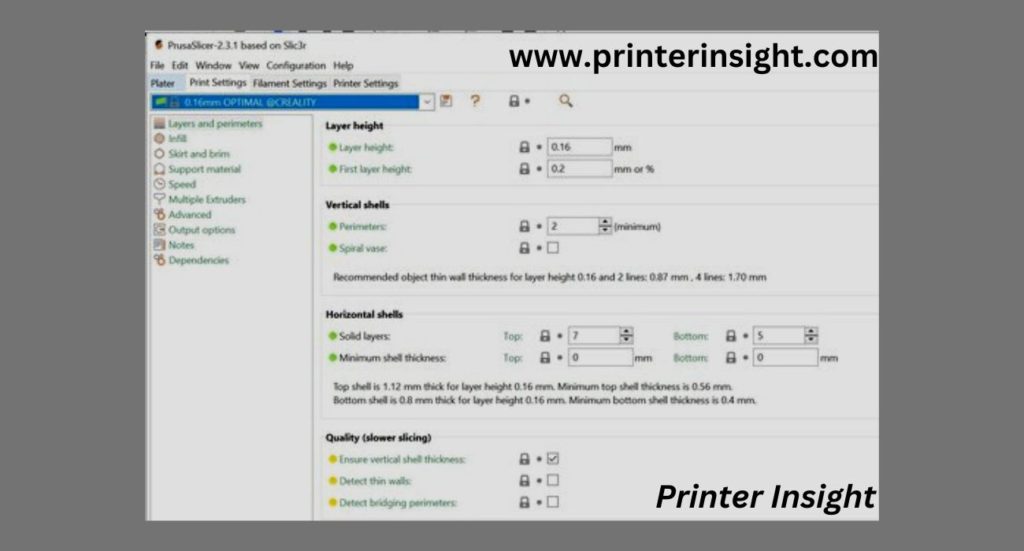
To achieve the greatest outcomes, you’ll really have to experiment with where the images are positioned on the printers.
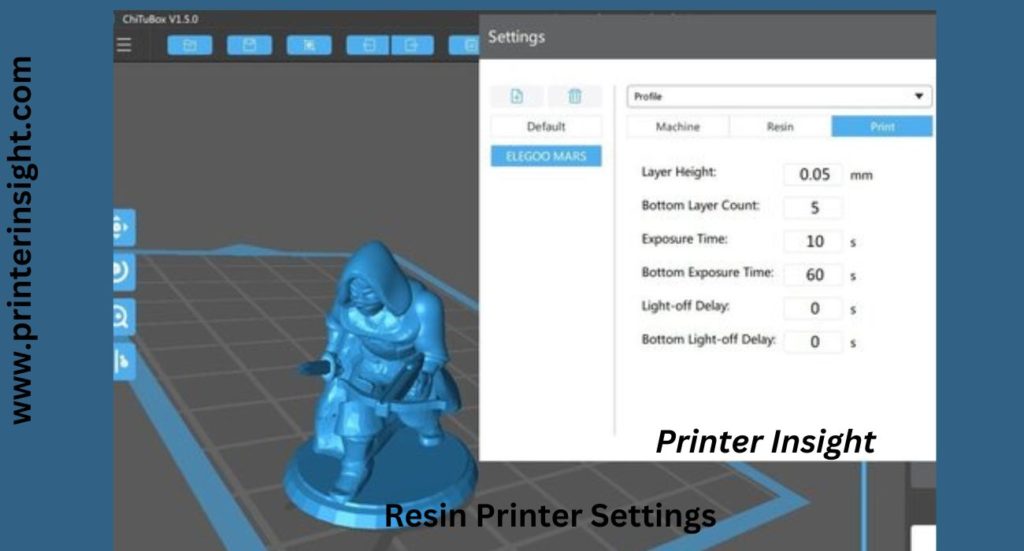
Resin printers require very few settings to set up, and once the printer is completed, it is simple to start printing. The layer duration (the amount of time per level is heated to UV light to cure) and the support material options are the only ones you’ll ever need to adjust.
3D Printer Resin Vs Filament Cost
We’ve already mentioned that the majority of FDM printers uses normal filament rolls.
Because filaments are inexpensive, nozzles would last for a year, and some versions offer extras in the packaging, 3D printers are more low-cost than SLA printers.
The fact that the resin and FEP layer in the resin bath must have been replenished considers resin 3D printers slightly elevated. If the resin container is too dusty for the printer to generate an accurate image, you just might have to rebuild it.
| Type of Filament | Per kg Cost ($) |
| Entry Level Filament (PLA, ABS, PETG) | 30-50 |
| Engineering Level (Nylon, PC, ASA) | 50-100 |
| Consumer Filament | 150 |
| Industrial Filament (PEEK) | 500 |
Over time, these adjustments get expensive. When lifting the created object from its own surface, users of both SLA 3D printers and FDM must repair the construction base if it is broken.
Besides, per kg cost of resin is comparatively higher than that of filament. But the smaller size of the best resin 3D printers minimizes this effect.
| Type of Resin | Per kg Cost ($) |
| Budget Resin | 20-35 |
| Engineering Level | 40 |
| SLA Resin | 175-300 |
| Biomedical Resin | 500 |
Another significant issue is maintenance cost, that is higher for resin 3D printers due to the use of safety equipment.
3D Printer Resin vs Filament Strength
Usually, filament 3D printers can deliver stronger and more durable 3D printed objects. But everything has exceptions.
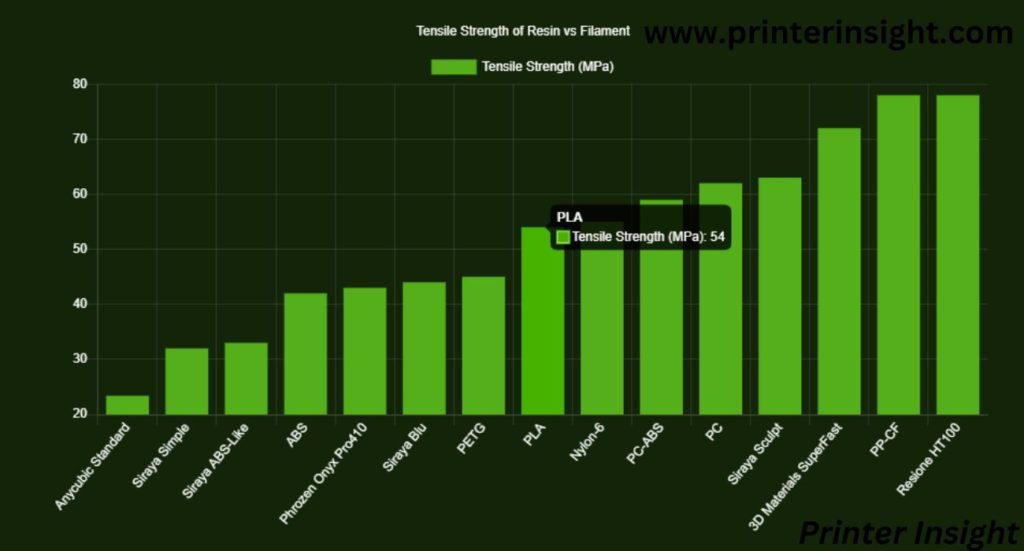
Siraya Tech Sculpt, a special resin, has similar robustness and tensile strength to PETG, which is tremendous. You must choose your 3D printer considering your project. In the case of resin vs filament miniatures, durable resin materials are more suitable options than their counterparts.
Build Volume
Filament printers are more advantageous than resin printers in the case of large object printing because of their larger build volume. The Creality Ender 3, a reputable FDM printer, has a build volume of 220 x 220 x 250 mm.
These two are large-volume FDM 3D printers.
On the other hand, resin printers offer a smaller build volume.
Creality Halot-One and Elegoo Mars: 130 x 80 x 160 mm (Entry Level)
Elegoo Saturn are 192 x 120 x 150 mm (Premium)
Preservation
The only visible change in a resin printer is the Z-axis leading bolt, which raises the rollers also as the pattern appears. As a result, they’re significantly less likely to have mechanical problems. Therefore, you can most definitely have to change a number of essential parts through the period:
- The FEP film at the bottom of something like the tank is prone to bending and tearing.
- Throughout the ages, the LCD may develop difficulties.
Because filament printers include motion sensors in all 3 directions, they will need to be replaced or tightened over time. These types of restorations are uncommon, according to our findings.
The filament path—the compressor that pulls the filament and the heat end that burns it just before dropping it across the portion of the majority of filament printer servicing.
- The extrusion plate, which interacts with the filament and drives one into the higher temperature, might wear down at some point.
- The heated end of the route elements degrade.
In general, filament printers demand more upkeep, although the difference isn’t significant.
Filament Features for FDM 3D Printing
For FDM printers, filaments serve as “3D printer ink.” Filaments can be summarized as follows:
- Reasonably priced
- Simple to get to
- Simple to work with.
- Materials come in a wide range of choices.
- Appropriate for hobbyists, amateurs, and newbies at the early phases of prototyping.
PLA and ABS are the most popular in the sector. These 3D printing elements come in a variety of colors and textures.
- a wide selection of hues (red, violet, black, orange, blue, white, etc.)
- Filaments with a length of approximately 1.65 mm and 1.98 mm
- widths of reels around (0.3 kg, 0.90 kg, 1.59 kg, 3.9 kg, 5 kg, 8 kg, 11 kg)
- Dimensional accuracy (-0.03, -0.01 mm)
Resin Features for SLA/DLP Printing
The resins are next. If you take this route, you will earn from the following:
- Enhanced clarity
- Details that are really accurate
- For post-processing, a water or isopropanol solution may be required.
- Colors and sizes come in a wide range of options.
Best Filament 3D Printer in 2023
We’ve compiled a list of 11 of Amazon’s best-rated 3D filaments though you can start printing right away.
- The best filament 3D printer (Best-Rated): SUNLU
- The best filament 3D printer (Best Cheap): TECBEARS
- The best filament 3D printer (Best PLA): OVERTURE
- The best filament 3D printer (Best Carbon Fiber): PROLINE
- The best filament 3D printer (Best Food Safe): OVERTURE
Best Resin 3D Printer in 2023
We’ve compiled a list of Amazon’s best-rated 3D resin though you can start printing right away.
- Generally, the best resin 3D printer is Elegoo Mars 2 Pro.
- Resin 3D printers of the highest quality: Phrozen Sonic Mini 8K
- The best resin 3D printer for wide form: Elegoo Saturn
- The top high resin 3D printer: Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K
- Of about $200, the best resin 3D printer is: Anycubic Photon Mono
FAQ
There are several customers frequently asked questions and responses you might find useful.
Is Filament Stronger Than Resin?
Because of their physical qualities, filament 3D printers are much stronger than resin 3D prints.
Is Filament Or Resin Faster?
Single-object printing is substantially faster with filament printers. However, when you insert a few more things, it will take longer. Resin printers, on the other hand, may print many things at the same time as a single item.
Is Resin Printing More Expensive Than Filament?
As you’ll see, resin seems to be more costly than filament, but the advantage of having a resin printer is completely obvious: better prints. When it comes to resin printing, there are many other things to consider in adding to that same printer and resin expenses.
Conclusion
What defines whether you purchase an SLA 3D printer or an FDM 3D printer is mostly decided by your required purpose.
If you’re searching for a device that can generate a bunch of cheap models in a small space of time and accuracy and outer layer polish aren’t key quality attributes, go with an FDM 3D printer.
If you’re making foundry forms for complex parts like accessories and design load-bearing capacity is not really a requirement, an SLA 3D printer is the way to go.




